In the intricate realm of diabetes management, understanding the nuances of blood sugar levels is the cornerstone of maintaining optimal health. Unlike the simplistic view of a singular “normal” range, the glycemic landscape for diabetics encompasses a dynamic spectrum influenced by factors such as meal timing, physical activity, and individual metabolic rates. This article aims to demystify the concept of healthy blood sugar levels for diabetics, providing a comprehensive guide that empowers individuals to take control of their glucose destiny.
D Blood Sugar Regulation
At the core of blood sugar management lies the delicate interplay between insulin, glucagon, and other key hormones. Insulin, a peptide hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas, acts as the “key” to unlocking cells. When glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, insulin binds to receptors on the surface of cells, triggering a series of biochemical reactions. This process enables glucose transporters (GLUT) to move to the cell membrane, facilitating the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into cells, where it is used for energy production through cellular respiration.
Defining the Target Ranges
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends specific target ranges for blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes. Before meals, also known as preprandial levels, the target range is typically between 80 to 130 mg/dL (4.4 to 7.2 mmol/L). This range helps ensure that there is enough glucose available for cells to function properly without causing excessive spikes after eating. Two hours after the start of a meal, or postprandial levels, the goal is to keep blood sugar levels below 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L). This limit is set to minimize the stress on blood vessels and organs caused by high glucose levels.
The Importance of Consistency
Consistency is key when it comes to managing blood sugar levels. Fluctuations in glucose levels can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe complications. When blood sugar levels drop too low (hypoglycemia), symptoms such as shakiness, sweating, rapid heartbeat, confusion, and even loss of consciousness can occur. On the other hand, persistently high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia) can cause fatigue, increased thirst, frequent urination, blurred vision, and over time, damage to nerves, blood vessels, and organs, leading to conditions like nerve damage (neuropathy), kidney disease (nephropathy), and eye problems (retinopathy).
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity is another essential component of diabetes management. Exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively, allowing glucose to enter cells and be used for energy. When muscles contract during physical activity, they can take up glucose from the bloodstream even without the presence of insulin, a process known as non-insulin-dependent glucose uptake. This helps lower blood sugar levels both during and after exercise.
Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, per week. Strength training exercises, such as weightlifting, can also be beneficial as they build muscle mass. Muscle tissue is more metabolically active and uses more glucose, contributing to better blood sugar control. However, it’s important to be aware that physical activity can sometimes cause blood sugar levels to drop, especially in individuals taking insulin or certain medications. Therefore, proper planning, such as adjusting insulin doses or having a snack before or after exercise, may be necessary.
Medications and Insulin
For many diabetics, medications and insulin are necessary to control blood sugar levels. There are several classes of diabetes medications, each working in different ways. Sulfonylureas, for example, stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. Metformin, one of the most commonly prescribed medications, works by improving insulin sensitivity in the body’s cells and reducing the amount of glucose produced by the liver. Thiazolidinediones enhance insulin sensitivity in fat, muscle, and liver cells, while DPP-4 inhibitors increase the body’s production of insulin and decrease the production of glucagon.
Stress and Illness
Stress and illness can also have a significant impact on blood sugar levels. When the body is under stress, whether it’s physical, emotional, or psychological, it releases hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones trigger the body’s “fight or flight” response, which includes increasing blood sugar levels by stimulating the liver to release glucose and reducing the effectiveness of insulin.
Similarly, during illness, the body’s immune response can interfere with insulin function. When the body is fighting an infection or dealing with inflammation, it releases cytokines, which can block insulin signaling and lead to elevated blood sugar levels. In addition, medications used to treat illnesses, such as corticosteroids, can also cause blood sugar levels to rise. Therefore, it’s important for diabetics to monitor their blood sugar levels more frequently during times of stress or illness and work with their healthcare provider to adjust their treatment plan if necessary.
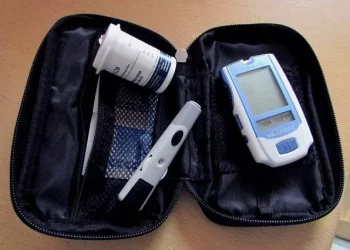
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG)
SMBG involves using a small blood sample, usually obtained by pricking the finger with a lancet, and testing it with a glucose meter. This method provides immediate results, allowing individuals to make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication. To perform an SMBG test, a drop of blood is placed on a test strip, which is then inserted into the glucose meter. The meter analyzes the blood sample and displays the blood sugar level within seconds.
SMBG is typically recommended for individuals taking insulin or other medications that can cause hypoglycemia. By checking their blood sugar levels before and after meals, before and after exercise, and at bedtime, they can ensure that their blood sugar remains within the target range. However, SMBG only provides a snapshot of blood sugar levels at a specific moment in time and may not capture all the fluctuations that occur throughout the day.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
CGM uses a small sensor inserted under the skin, usually on the abdomen or arm, to continuously measure blood sugar levels. The sensor is connected to a transmitter that sends real-time data to a monitor or smartphone app. CGM provides a more comprehensive view of blood sugar patterns over time, including how quickly blood sugar levels rise and fall, and how long they stay outside the target range.
Hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c) Test
The HbA1c test measures the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. When glucose is present in the bloodstream, it attaches to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells. The longer the glucose remains in the blood, the more it binds to hemoglobin. Since red blood cells have a lifespan of about 120 days, the HbA1c test reflects the average blood sugar level over this period.
This test provides a long-term assessment of diabetes control and is used to diagnose diabetes, monitor treatment effectiveness, and set treatment goals. The ADA recommends that individuals with diabetes aim for an HbA1c level of less than 7%. However, the target HbA1c level may vary depending on individual circumstances, such as age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions. A lower HbA1c level generally indicates better blood sugar control and a reduced risk of complications.
Follow a Balanced Diet
A balanced diet is essential for managing blood sugar levels. Focus on consuming a variety of nutrient-dense foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Fruits and vegetables are rich in fiber, vitamins, and minerals, and their natural sugars are absorbed more slowly due to the fiber content. Whole grains, such as brown rice, quinoa, and whole wheat bread, are a good source of complex carbohydrates and fiber, which help regulate blood sugar levels.
Lean proteins, such as chicken, fish, beans, and low-fat dairy products, can help keep you feeling full and satisfied while having a minimal impact on blood sugar. Healthy fats, such as those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil, can also be beneficial as they can help slow the absorption of carbohydrates. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary beverages, and foods high in saturated and trans fats, as these can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels and contribute to weight gain and other health problems.
Conclusion
Maintaining healthy blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of diabetes management. By understanding the target ranges, the factors that influence blood sugar levels, and the importance of regular monitoring, individuals with diabetes can take proactive steps to control their glucose levels and reduce their risk of complications. Remember, diabetes management is a journey, and with the right knowledge, support, and lifestyle choices, you can live a healthy, fulfilling life. Regular communication with your healthcare team, combined with self-care practices, will help you stay on track and achieve your diabetes management goals.o