Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels that develop during pregnancy and typically resolve after giving birth. Managing gestational diabetes effectively is crucial for the health of both the mother and the baby. One of the key aspects of managing GDM is understanding what constitutes a “good” blood sugar level. This article will delve into the optimal blood sugar levels for gestational diabetes tests, the significance of these levels, and how to maintain them through lifestyle and medical interventions.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when the body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively during pregnancy. This condition affects approximately 2-10% of pregnancies in the United States. While the exact cause of GDM is not known, it is believed that the hormones produced during pregnancy can interfere with the body’s ability to use insulin effectively, leading to insulin resistance.
Why is Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels Important?
Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for preventing complications associated with gestational diabetes. High blood sugar levels can pose risks to both the mother and the baby, including:
- For the Mother: Increased risk of preeclampsia, cesarean delivery, and developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- For the Baby: Macrosomia (large birth weight), hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) after birth, respiratory distress syndrome, and a higher risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes in the future.
Optimal Blood Sugar Levels for Gestational Diabetes
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) and other health organizations have established specific blood sugar targets for pregnant women with gestational diabetes. These targets help ensure that blood sugar levels remain within a safe range to minimize risks.
Fasting Blood Sugar Levels
The fasting blood sugar level is measured after an overnight fast, usually before breakfast. For women with gestational diabetes, the target fasting blood sugar level is typically:
- Less than 95 mg/dL (5.3 mmol/L)
Maintaining fasting blood sugar levels below this threshold helps reduce the risk of complications.
Postprandial Blood Sugar Levels
Postprandial blood sugar levels are measured after meals. These measurements help determine how well the body is managing blood sugar levels in response to food intake. The targets for postprandial blood sugar levels are:
- One hour after a meal: Less than 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L)
- Two hours after a meal: Less than 120 mg/dL (6.7 mmol/L)
Monitoring postprandial blood sugar levels ensures that the body is effectively processing glucose from meals.
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) is a standard diagnostic tool for gestational diabetes. It involves measuring blood sugar levels after consuming a glucose-rich drink. The typical thresholds for diagnosing gestational diabetes using the OGTT are:
- Fasting: 92 mg/dL (5.1 mmol/L) or higher
- One hour after glucose drink: 180 mg/dL (10.0 mmol/L) or higher
- Two hours after glucose drink: 153 mg/dL (8.5 mmol/L) or higher
If any of these values are met or exceeded, a diagnosis of gestational diabetes is made.
Maintaining Optimal Blood Sugar Levels
Managing gestational diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and sometimes medication. Here are some strategies to maintain optimal blood sugar levels:
Dietary Management
A balanced diet is crucial for managing blood sugar levels. Key dietary recommendations include:
- Carbohydrate Control: Focus on complex carbohydrates with a low glycemic index, such as whole grains, vegetables, and legumes. Limit simple sugars and refined carbohydrates.
- Portion Control: Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Balanced Nutrients: Ensure meals include a balance of carbohydrates, proteins, and healthy fats to stabilize blood sugar levels.
- Fiber Intake: High-fiber foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, can help slow glucose absorption and prevent spikes in blood sugar.
Physical Activity
Regular physical activity can improve insulin sensitivity and help regulate blood sugar levels. Recommended activities include:
- Aerobic Exercise: Walking, swimming, or other moderate-intensity aerobic exercises for at least 30 minutes most days of the week.
- Strength Training: Incorporating strength training exercises can also help improve insulin sensitivity.
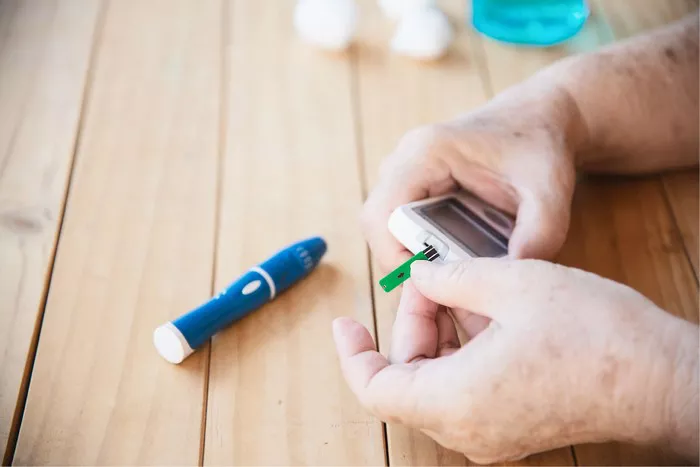
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for managing gestational diabetes. This typically involves:
- Self-Monitoring: Using a blood glucose meter to check blood sugar levels at home. This helps identify patterns and adjust diet or activity as needed.
- Regular Check-Ups: Frequent visits to a healthcare provider to review blood sugar logs and adjust the management plan.
Medication
In some cases, lifestyle modifications may not be enough to maintain optimal blood sugar levels, and medication may be required. Common medications include:
- Insulin: The most commonly used medication for gestational diabetes, as it does not cross the placenta and is safe for the baby.
- Oral Medications: Metformin and glyburide are sometimes used, though insulin is preferred if these are not sufficient.
Potential Complications and Their Management
Despite best efforts, some women with gestational diabetes may still experience complications. Understanding these potential issues and their management is crucial:
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, can occur if blood sugar levels drop too low. Symptoms include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and dizziness. Management includes:
- Immediate Treatment: Consuming 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or fruit juice.
- Prevention: Regular monitoring and ensuring meals and snacks are balanced.
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, can pose risks if not managed properly. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and blurred vision. Management includes:
- Adjusting Diet: Reducing carbohydrate intake and focusing on foods with a low glycemic index.
- Medication: Adjusting insulin doses or oral medications as prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Long-Term Considerations
While gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth, it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Long-term considerations include:
Postpartum Screening
Women who have had gestational diabetes should undergo postpartum screening to ensure blood sugar levels return to normal. This typically involves:
- OGTT: Conducted 6-12 weeks postpartum to check for persistent diabetes or prediabetes.
- Regular Monitoring: Annual or biannual blood sugar testing to monitor for type 2 diabetes.
Healthy Lifestyle
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle postpartum can help reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Recommendations include:
- Balanced Diet: Continuing to follow a healthy eating plan.
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity.
- Weight Management: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight.
See also: What Are The Various Aspects Of Gestational Diabetes?
Conclusion
Managing gestational diabetes effectively is crucial for the health of both the mother and the baby. Understanding what constitutes a good number for gestational diabetes tests and how to maintain optimal blood sugar levels can help prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy and delivery. Through a combination of dietary management, physical activity, regular monitoring, and medical interventions, women with gestational diabetes can achieve and maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Postpartum care and long-term lifestyle changes are also essential to reduce the risk of future health issues. By staying informed and proactive, women with gestational diabetes can navigate their pregnancies safely and healthily.
Related topics:
How to Manage Gestational Diabetes
What’s the Warning Signs and Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes