The Role of Glucose Monitoring in Diabetes Management
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by the body’s inability to properly regulate blood glucose levels. There are two main types of diabetes: Type 1 diabetes, where the body fails to produce insulin, and Type 2 diabetes, where the body either resists the effects of insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. Regardless of the type, maintaining blood glucose levels within a target range is crucial to prevent complications such as cardiovascular diseases, neuropathy, retinopathy, and kidney damage.
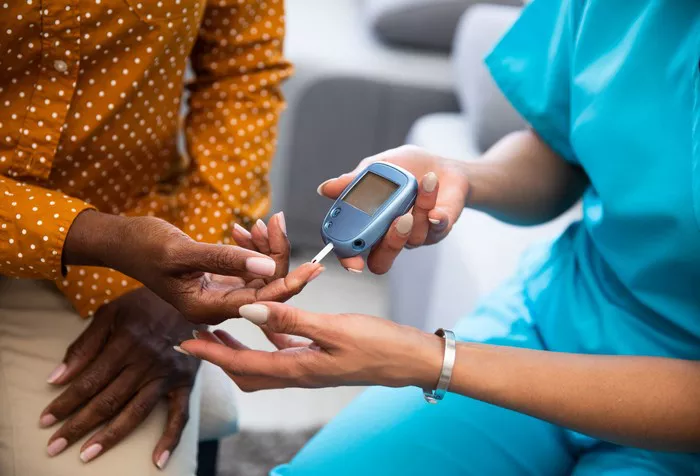
A glucose monitor measures the concentration of glucose in the blood, providing immediate feedback to the user. This information helps individuals with diabetes make informed decisions about their diet, physical activity, and medication. Regular monitoring enables timely adjustments to treatment plans, reducing the risk of both hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) and hypoglycemia (low blood sugar).
Types of Glucose Monitors
1. Traditional Blood Glucose Meters
Traditional blood glucose meters are the most commonly used devices for monitoring blood sugar levels. These meters require a small blood sample, usually obtained from a fingertip prick. The blood sample is placed on a test strip, which the meter reads to determine the blood glucose level. These meters are known for their accuracy and reliability, making them a staple in diabetes management.
2. Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Continuous glucose monitors are advanced devices that provide real-time glucose readings throughout the day and night. A small sensor is inserted under the skin, typically on the abdomen or arm, which measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. CGMs transmit data to a receiver or a smartphone app, allowing users to track their glucose levels continuously. This technology offers valuable insights into glucose trends and patterns, helping users and healthcare providers make more informed treatment decisions.
3. Flash Glucose Monitoring Systems
Flash glucose monitors are similar to CGMs but require the user to scan the sensor with a reader or smartphone to obtain glucose readings. The sensor can be worn for up to 14 days, providing a convenient and less invasive option for glucose monitoring. Flash glucose monitoring systems offer a compromise between traditional meters and CGMs, combining ease of use with detailed glucose data.
How Do Glucose Monitors Work?
The Science Behind Glucose Monitoring
Glucose monitors operate on the principle of electrochemical detection. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how these devices work:
1. Blood Sample Collection
For traditional blood glucose meters, a lancet is used to prick the skin, usually on the fingertip, to obtain a small blood sample. The blood sample is then placed on a disposable test strip.
2. Chemical Reaction
The test strip contains an enzyme called glucose oxidase or glucose dehydrogenase. When blood is applied to the strip, the glucose in the blood reacts with the enzyme, producing an electrical current proportional to the glucose concentration.
3. Electrical Signal Conversion
The meter measures the electrical current generated by the chemical reaction. This current is then converted into a digital reading, which represents the blood glucose level.
4. Data Display
The blood glucose level is displayed on the meter’s screen, usually within a few seconds. Some advanced meters can store readings and provide averages over specific periods, such as 7, 14, or 30 days.
For continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitoring systems, the process is slightly different:
1. Sensor Insertion
A small sensor is inserted under the skin using an applicator. The sensor measures glucose levels in the interstitial fluid, which reflects blood glucose levels with a slight delay.
2. Data Transmission
The sensor continuously measures glucose levels and transmits the data to a receiver, smartphone app, or reader. In the case of flash glucose monitors, the user scans the sensor to obtain a reading.
3. Glucose Trend Analysis
CGMs and flash glucose monitors provide continuous or on-demand glucose readings, displaying trends and patterns over time. This data helps users and healthcare providers identify fluctuations and make necessary adjustments to treatment plans.
Benefits of Using Glucose Monitors
Empowering Patients with Information
Glucose monitors offer numerous benefits, empowering patients to take control of their diabetes management. Some key advantages include:
1. Real-Time Feedback
Glucose monitors provide immediate feedback on blood glucose levels, allowing users to respond promptly to changes. This real-time information is crucial for preventing both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, reducing the risk of complications.
2. Improved Glycemic Control
Regular monitoring helps individuals with diabetes maintain better glycemic control. By tracking glucose levels consistently, users can identify patterns and make informed decisions about their diet, exercise, and medication.
3. Enhanced Quality of Life
With accurate glucose data at their fingertips, individuals with diabetes can lead more active and flexible lives. They can make timely adjustments to their lifestyle, reducing the burden of managing their condition.
4. Early Detection of Trends
Continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitoring systems provide valuable insights into glucose trends and patterns. This information helps users and healthcare providers detect potential issues early, enabling proactive interventions.
Challenges and Limitations
Addressing the Drawbacks of Glucose Monitoring
While glucose monitors are invaluable tools for diabetes management, they are not without challenges and limitations. Understanding these drawbacks is essential for optimizing their use and addressing patient concerns.
1. Cost
The cost of glucose monitoring devices and supplies can be a significant barrier for many individuals. Traditional blood glucose meters require regular purchase of test strips and lancets, while CGMs and flash glucose monitors involve the cost of sensors and readers. Insurance coverage varies, and out-of-pocket expenses can add up over time.
2. Accuracy
Although glucose monitors are generally accurate, factors such as user error, test strip quality, and device calibration can affect readings. Continuous glucose monitors may also have a slight lag in reflecting rapid changes in blood glucose levels, leading to discrepancies between interstitial and blood glucose measurements.
3. Invasiveness
Traditional blood glucose monitoring involves finger pricks, which can be uncomfortable and inconvenient for users. Continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitoring systems reduce the need for frequent finger pricks but still require sensor insertion, which may cause discomfort for some individuals.
4. Data Overload
Continuous glucose monitors provide a wealth of data, which can be overwhelming for some users. Interpreting glucose trends and making informed decisions based on this data requires a certain level of understanding and education.
Innovations in Glucose Monitoring
Advancements Shaping the Future of Diabetes Care
The field of glucose monitoring is continually evolving, with innovations aimed at improving accuracy, convenience, and user experience. Some notable advancements include:
1. Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
Researchers are exploring non-invasive glucose monitoring technologies that eliminate the need for blood samples or sensor insertion. These technologies include optical sensors, transdermal patches, and saliva-based glucose measurements. While still in development, non-invasive methods hold promise for enhancing comfort and compliance.
2. Integrated Insulin Pumps and CGMs
The integration of insulin pumps with continuous glucose monitors has revolutionized diabetes management. These systems, known as closed-loop or artificial pancreas systems, automatically adjust insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings. This closed-loop approach mimics the body’s natural insulin regulation, improving glycemic control and reducing the burden of manual adjustments.
3. Smartwatch Integration
Wearable technology, such as smartwatches, is being integrated with glucose monitoring systems to provide seamless and discreet glucose tracking. Smartwatches can receive glucose data from CGMs and flash glucose monitors, displaying readings and alerts directly on the user’s wrist. This integration enhances convenience and accessibility, allowing users to monitor their glucose levels on the go.
4. Advanced Data Analytics
Advancements in data analytics and machine learning are transforming the way glucose data is interpreted. Smart algorithms can analyze glucose trends, predict future glucose levels, and provide personalized recommendations for diabetes management. These insights help users and healthcare providers make proactive and informed decisions.
Practical Tips for Using Glucose Monitors
Maximizing the Benefits of Glucose Monitoring
To optimize the use of glucose monitors, individuals with diabetes should follow practical tips and best practices:
1. Regular Calibration
For continuous glucose monitors, regular calibration is essential to ensure accurate readings. Users should follow the manufacturer’s instructions for calibration, typically involving a comparison with a traditional blood glucose meter.
2. Proper Technique
When using traditional blood glucose meters, proper technique is crucial for accurate results. Users should wash their hands before testing, use the correct amount of blood, and avoid squeezing the finger excessively, which can dilute the blood sample.
3. Consistent Monitoring
Consistency is key in glucose monitoring. Individuals should monitor their blood glucose levels at regular intervals, as recommended by their healthcare provider. Regular monitoring helps identify patterns and make informed decisions.
4. Understanding Trends
Continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitors provide valuable trend data. Users should take the time to understand these trends and discuss them with their healthcare provider. Recognizing patterns in glucose levels can help fine-tune treatment plans and prevent complications.
5. Staying Informed
Diabetes management is an ongoing process, and staying informed about the latest advancements in glucose monitoring is essential. Individuals should attend diabetes education programs, read reputable sources, and engage with their healthcare team to stay up to date.
See also: What’s the Cheapest Blood Glucose Meter
Conclusion
The Future of Glucose Monitoring
Glucose monitors have revolutionized diabetes management, providing individuals with the tools they need to maintain optimal blood glucose levels and improve their quality of life. From traditional blood glucose meters to continuous glucose monitors and flash glucose monitoring systems, these devices offer valuable insights and real-time feedback.
While challenges and limitations exist, ongoing innovations in glucose monitoring technology are addressing these issues and shaping the future of diabetes care. As non-invasive methods, integrated systems, and advanced data analytics continue to evolve, glucose monitoring will become even more accurate, convenient, and user-friendly.
For individuals with diabetes, understanding how glucose monitors work and how to use them effectively is crucial for achieving better glycemic control and preventing complications. By staying informed and proactive, individuals can take charge of their diabetes management and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives.
Related topics:
What Is the Right Number for Blood Sugar Levels?
How the Freestyle Glucose Monitor Works: A Comprehensive Guide