Sugar, particularly in the context of blood glucose levels and dietary intake, plays a critical role in our health. Understanding the best levels of sugar for optimal health involves examining both blood glucose levels and dietary sugar consumption. This comprehensive article delves into the scientific research and medical guidelines to provide a clear understanding of the best levels of sugar for maintaining good health.
Optimal Blood Glucose Levels
Understanding Blood Glucose Homeostasis
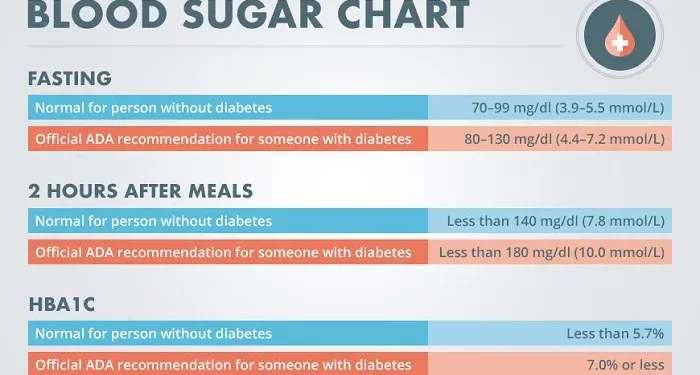
Blood glucose levels are a vital health metric, especially for individuals with diabetes. The body tightly regulates blood glucose to provide a steady supply of energy to the brain and other organs. Normal fasting blood glucose levels are below 5.6 mmol/L (100 mg/dL), and normal 2-hour post-meal glucose levels range from 3.8 to 7.7 mmol/L (70 to 139 mg/dL) .
Targeting Optimal Glucose Levels for Health
While normal glucose levels serve as a reference, NOVI Health proposes more stringent target levels known as “optimal” glucose levels. Optimal fasting blood glucose levels are suggested to be 3.3 to 5 mmol/L (60 to 90 mg/dL), and the optimal post-meal glucose peak should be below 6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL), with a maximum of a 1.5 mmol/L (30 mg/dL) increase in glucose levels post-meal .
Dietary Sugar Intake: The WHO Recommendations
The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends reducing daily intake of free sugars to less than 10% of total energy intake, with a further reduction to below 5% or roughly 25 grams (6 teaspoons) per day providing additional health benefits . Free sugars include monosaccharides and disaccharides added to foods and drinks by the manufacturer, cook, or consumer, and sugars naturally present in honey, syrups, fruit juices, and fruit juice concentrates.
Health Impacts of Dietary Sugar Consumption
Endocrine and Metabolic Outcomes
High dietary sugar consumption has been linked to harmful associations with endocrine and metabolic outcomes, cardiovascular outcomes, cancer outcomes, and other outcomes such as neuropsychiatric, dental, hepatic, osteal, and allergic issues . This underscores the importance of moderating sugar intake to mitigate these risks.
Cardiovascular Disease and Sugar Intake
Research indicates that each 250 mL/day increment of sugar-sweetened beverage consumption is associated with a 17% higher risk of coronary heart disease . This highlights the cardiovascular risks associated with high sugar intake, particularly from sugar-sweetened beverages.
Gout and Sugar-Sweetened Beverages
Low quality evidence suggests that each serving/week increment of sugar-sweetened beverage consumption is associated with a 4% higher risk of gout . This further emphasizes the need for moderation in sugar intake, especially in the form of beverages.
Pancreatic Cancer and Fructose Consumption
Every 25 g/day increment of fructose consumption is associated with a 22% higher risk of pancreatic cancer . This finding points to the potential long-term health risks of high fructose intake.
Conclusion
The best level of sugar for optimal health involves maintaining optimal blood glucose levels and moderating dietary sugar intake. For blood glucose, the optimal fasting level is 3.3 to 5 mmol/L (60 to 90 mg/dL), and the optimal post-meal glucose peak should be below 6.1 mmol/L (110 mg/dL), with a maximum of a 1.5 mmol/L (30 mg/dL) increase post-meal . In terms of dietary sugar, the WHO recommends reducing intake to less than 10% of total energy intake, with additional benefits at a reduction to below 5% or roughly 25 grams (6 teaspoons) per day . Exceeding these levels can lead to a range of health complications, including cardiovascular disease, gout, and an increased risk of certain cancers. It is clear that maintaining optimal sugar levels is crucial for preventing disease and promoting health and well-being.
Related topics