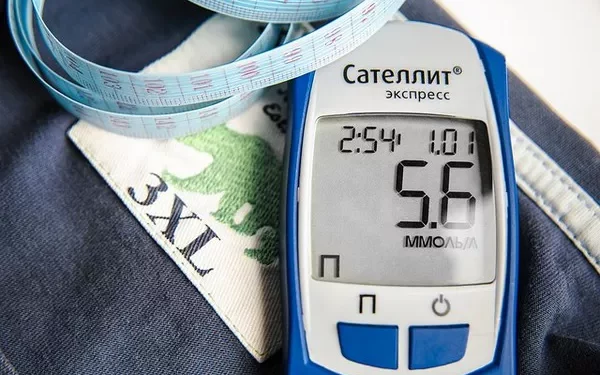
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a condition that occurs when blood glucose levels drop below normal. While it is commonly associated with diabetes, particularly type 1 diabetes, hypoglycemia can also occur in individuals with type 2 diabetes. Understanding and managing type 2 hypoglycemia is crucial for maintaining overall health and preventing complications. This article provides a comprehensive overview of type 2 hypoglycemia, its causes, symptoms, treatment, and prevention strategies.
Understanding Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is defined by blood glucose levels falling below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). It can occur as a result of various factors, including excessive insulin or medication use, insufficient food intake, increased physical activity, or alcohol consumption. Symptoms of hypoglycemia can range from mild to severe and include shakiness, sweating, confusion, dizziness, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness or seizures.
Type 2 Diabetes and Hypoglycemia
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by insulin resistance and, often, decreased insulin production over time. Individuals with type 2 diabetes manage their condition through lifestyle modifications, oral medications, and sometimes insulin therapy. Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes can be particularly concerning as it may lead to serious health risks if not promptly addressed.
Causes of Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Medication-Induced Hypoglycemia
Certain medications used to treat type 2 diabetes can increase the risk of hypoglycemia. These include:
Insulin: Insulin therapy, especially if not properly dosed, can lead to low blood sugar levels.
Sulfonylureas: These oral medications stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin and can cause hypoglycemia if blood sugar levels drop too low.
Meglitinides: Similar to sulfonylureas, meglitinides increase insulin production and can lead to hypoglycemia.
Dietary Factors
Inadequate food intake or irregular meal patterns can contribute to hypoglycemia. Skipping meals, consuming insufficient carbohydrates, or not adjusting food intake to match medication can result in low blood sugar levels.
Physical Activity
Increased physical activity can lower blood glucose levels as muscles use more glucose for energy. Without proper adjustments in food intake or medication, exercise can lead to hypoglycemia.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can interfere with the liver’s ability to release glucose into the bloodstream, increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. Drinking alcohol without eating can further exacerbate this risk.
Other Health Conditions
Certain medical conditions, such as kidney disease or hormonal deficiencies, can affect blood sugar regulation and increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
Recognizing the symptoms of hypoglycemia is crucial for prompt treatment. Symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the hypoglycemia and the individual’s response. Common symptoms include:
Mild Hypoglycemia: Shakiness, sweating, hunger, dizziness, irritability, and rapid heartbeat.
Moderate Hypoglycemia: Confusion, blurred vision, difficulty concentrating, weakness, and fatigue.
Severe Hypoglycemia: Seizures, loss of consciousness, and in extreme cases, coma or death.
Diagnosing Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is typically diagnosed through blood glucose testing. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can help identify episodes of low blood sugar and determine their frequency and causes.
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Patients should regularly check their blood sugar levels using a glucometer, especially if they experience symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): CGM devices provide real-time glucose readings and trends, helping to detect and manage hypoglycemia more effectively.
Treatment of Hypoglycemia
Prompt treatment of hypoglycemia is essential to prevent severe complications. The primary goal is to raise blood glucose levels to a safe range.
Immediate Treatment
The “15-15 Rule” is a commonly recommended method for treating mild to moderate hypoglycemia:
Consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates: This can include glucose tablets, gel, fruit juice, regular soda, or candy.
Wait 15 minutes: Allow time for the glucose to be absorbed and check blood sugar levels.
Repeat if necessary: If blood sugar levels remain below 70 mg/dL, consume another 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates and recheck after 15 minutes.
Severe Hypoglycemia
For severe hypoglycemia, where the individual is unable to consume carbohydrates orally or is unconscious, glucagon injections are necessary. Glucagon is a hormone that stimulates the liver to release glucose into the bloodstream.
Glucagon Kits: Patients and their caregivers should be trained in using glucagon kits, which are available as injectable or nasal forms.
Emergency Medical Services: If glucagon is not available or the individual does not respond to treatment, seek emergency medical assistance immediately.
Preventing Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes
Preventing hypoglycemia involves careful management of diabetes and awareness of factors that can affect blood sugar levels. Strategies for prevention include:
Medication Management
Proper Dosing: Ensure that insulin and oral medications are dosed correctly based on blood glucose levels, food intake, and physical activity.
Adjustments: Work with healthcare providers to adjust medication regimens during periods of increased physical activity, illness, or changes in routine.
Regular Monitoring
Frequent Blood Glucose Checks: Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to detect and address low blood sugar early.
CGM Use: Consider using continuous glucose monitoring systems to track glucose levels in real-time and identify trends.
Dietary Strategies
Consistent Meal Patterns: Eat regular meals and snacks to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Carbohydrate Counting: Balance carbohydrate intake with medication and physical activity to prevent low blood sugar.
Snacks: Carry quick sources of glucose, such as glucose tablets or candy, to treat unexpected hypoglycemia.
Exercise Precautions
Pre-Exercise Snacks: Consume a snack before engaging in physical activity, especially if blood sugar levels are on the lower side.
Monitor During Exercise: Check blood sugar levels before, during, and after exercise to ensure they remain within a safe range.
Alcohol Consumption
Moderation: Limit alcohol intake and never drink on an empty stomach.
Monitoring: Check blood sugar levels before and after drinking alcohol.
Education and Awareness
Patient Education: Educate patients about the signs, symptoms, and treatment of hypoglycemia.
Emergency Plans: Develop and share emergency plans with family members, friends, and caregivers to ensure prompt treatment of severe hypoglycemia.
Complications of Hypoglycemia
Untreated or recurrent hypoglycemia can lead to several complications, including:
Cognitive Impairment: Frequent episodes of hypoglycemia can affect cognitive function and memory.
Hypoglycemia Unawareness: Repeated hypoglycemia can reduce the body’s ability to recognize low blood sugar symptoms, increasing the risk of severe episodes.
Cardiovascular Events: Severe hypoglycemia can increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
Injury: Hypoglycemia can cause falls, accidents, and injuries due to confusion and loss of coordination.
Long-Term Management of Type 2 Hypoglycemia
Effective long-term management of hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes involves a comprehensive approach that includes lifestyle modifications, medication management, and regular monitoring.
Individualized Treatment Plans
Personalized Care: Work with healthcare providers to develop individualized diabetes management plans that address the specific needs and risks of each patient.
Regular Follow-Ups: Schedule regular follow-up appointments to review and adjust treatment plans as needed.
Advanced Monitoring Technologies
CGM Systems: Continuous glucose monitoring systems provide valuable data for managing blood sugar levels and preventing hypoglycemia.
Insulin Pumps: For patients requiring insulin therapy, insulin pumps can deliver precise doses and adjust insulin delivery based on glucose readings.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy Eating: Follow a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
Physical Activity: Engage in regular physical activity that is safe and well-planned to prevent low blood sugar.
Stress Management
Relaxation Techniques: Practice relaxation techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing to manage stress, which can affect blood sugar levels.
Support Systems: Seek support from family, friends, or support groups to help manage diabetes and prevent hypoglycemia.
See also: What are the Causes of Sudden Hypoglycemia
Conclusion
Type 2 hypoglycemia is a critical aspect of diabetes management that requires careful attention and prompt treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for hypoglycemia can help individuals with type 2 diabetes maintain stable blood sugar levels and prevent complications. By implementing strategies for prevention, monitoring blood glucose levels regularly, and working closely with healthcare providers, patients can effectively manage hypoglycemia and improve their overall health and well-being.
Related topics: