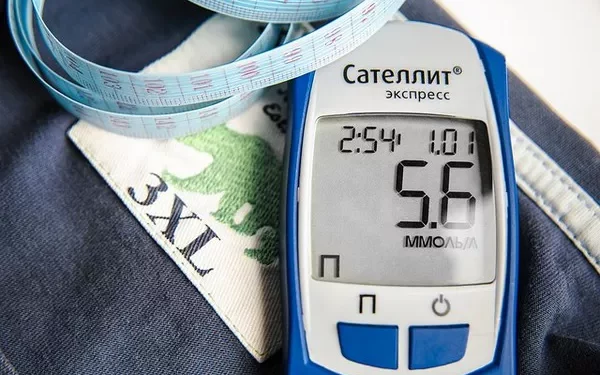
Hypoglycemia, commonly known as low blood sugar, is a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of glucose in the blood. It is a significant concern for individuals with diabetes but can also affect those without diabetes under certain conditions. Hypoglycemia can lead to a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe medical emergencies. Understanding why people get hypoglycemia is crucial for effective prevention and management. This article delves into the various causes, risk factors, and preventive measures associated with hypoglycemia.
The Physiology of Blood Glucose Regulation
To comprehend the mechanisms leading to hypoglycemia, it is essential first to understand how blood glucose is regulated. The human body maintains blood glucose levels within a narrow range, primarily through the actions of insulin and glucagon, hormones produced by the pancreas.
Insulin and Glucagon: The Balancing Act
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas in response to elevated blood glucose levels, such as after eating. It facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells for energy production and storage as glycogen in the liver and muscles. On the other hand, glucagon is released by the alpha cells of the pancreas when blood glucose levels drop, stimulating the release of glucose from glycogen stores in the liver into the bloodstream.
Other Hormones Involved
Besides insulin and glucagon, other hormones such as adrenaline, cortisol, and growth hormone also play roles in blood glucose regulation. These hormones are typically involved in the body’s response to stress and can increase blood glucose levels by promoting gluconeogenesis (the production of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources) and glycogenolysis (the breakdown of glycogen into glucose).
Primary Causes of Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can occur due to several underlying causes, broadly categorized into those related to diabetes management and those unrelated to diabetes.
Diabetes-Related Causes
Insulin Overdose
One of the most common causes of hypoglycemia in individuals with diabetes is an overdose of insulin. This can happen if too much insulin is administered, whether through injection or an insulin pump. Insulin overdose can rapidly decrease blood glucose levels, especially if not accompanied by adequate carbohydrate intake.
Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
Certain oral medications for diabetes, such as sulfonylureas and meglitinides, stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. An excess dose of these medications can lead to hypoglycemia, particularly if meals are skipped or delayed.
Mismatched Food Intake and Medication
For individuals with diabetes, maintaining a balance between medication, food intake, and physical activity is crucial. Hypoglycemia can occur if there is a mismatch, such as taking insulin or oral hypoglycemic agents without eating enough carbohydrates or exercising more intensely than usual without adjusting the medication dosage.
Non-Diabetes-Related Causes
Fasting and Starvation
Prolonged fasting or starvation can deplete the body’s glycogen stores, leading to hypoglycemia. This is because, in the absence of dietary glucose, the liver’s glycogen stores become the primary source of blood glucose. Once these stores are exhausted, blood glucose levels can drop significantly.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol can cause hypoglycemia by inhibiting gluconeogenesis in the liver. When alcohol is consumed in excess, especially on an empty stomach, it can prevent the liver from producing glucose, leading to a drop in blood sugar levels.
Severe Illnesses
Certain severe illnesses, such as sepsis or liver disease, can impair the body’s ability to regulate blood glucose levels. Sepsis, a severe infection that spreads throughout the body, can lead to hypoglycemia due to increased metabolic demands and impaired glucose production. Liver diseases can affect the liver’s capacity to store and release glucose.
Hormonal Deficiencies
Deficiencies in hormones such as cortisol and growth hormone can result in hypoglycemia. These hormones play roles in stimulating glucose production and maintaining blood glucose levels. Conditions such as Addison’s disease (adrenal insufficiency) or hypopituitarism (insufficient pituitary gland function) can lead to inadequate hormone production and subsequent hypoglycemia.
Insulinoma
An insulinoma is a rare tumor of the pancreas that produces excess insulin. This overproduction of insulin can lead to recurrent episodes of hypoglycemia, often unrelated to food intake or other external factors.
Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
Understanding the risk factors for hypoglycemia can help in identifying individuals who are more susceptible to this condition and implementing preventive strategies.
Diabetes Management
Intensive Insulin Therapy
Patients with diabetes who are on intensive insulin therapy, involving multiple daily injections or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (insulin pumps), are at higher risk for hypoglycemia. The precise titration of insulin doses can sometimes lead to inadvertent overdoses, especially when combined with variations in diet and physical activity.
Advanced Age
Older adults with diabetes are at an increased risk of hypoglycemia. This is due to several factors, including age-related decline in renal function, which affects insulin clearance, and a decreased ability to recognize and respond to hypoglycemic symptoms.
Lifestyle Factors
Irregular Eating Patterns
Individuals with irregular eating patterns or those who skip meals are at a higher risk of hypoglycemia. Consistent meal timing helps in maintaining stable blood glucose levels, and skipping meals can disrupt this balance, leading to low blood sugar.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
As previously mentioned, excessive alcohol consumption, particularly on an empty stomach, can precipitate hypoglycemia by inhibiting gluconeogenesis.
High Levels of Physical Activity
Intense or prolonged physical activity increases glucose uptake by the muscles, which can lead to hypoglycemia if carbohydrate intake is not adjusted accordingly. This is particularly relevant for individuals with diabetes who need to balance insulin doses with their activity levels.
Medical Conditions
Renal Impairment
Chronic kidney disease can increase the risk of hypoglycemia, especially in individuals with diabetes. Reduced kidney function affects insulin clearance, leading to prolonged insulin action and an increased risk of hypoglycemia.
Endocrine Disorders
As mentioned earlier, conditions affecting the adrenal glands, pituitary gland, or other endocrine organs can lead to hormonal imbalances that precipitate hypoglycemia.
Medications
Sulfonylureas and Meglitinides
These oral hypoglycemic agents are associated with a higher risk of hypoglycemia due to their mechanism of stimulating insulin secretion.
Non-Diabetic Medications
Certain medications not intended for diabetes management can also cause hypoglycemia. These include beta-blockers, which can mask hypoglycemia symptoms, and quinine, which is used to treat malaria but can lower blood glucose levels.
Symptoms and Signs of Hypoglycemia
Recognizing the symptoms and signs of hypoglycemia is vital for timely intervention. Hypoglycemia can present with a wide range of symptoms, which can be categorized into adrenergic (related to the activation of the sympathetic nervous system) and neuroglycopenic (related to a deficiency of glucose in the brain) symptoms.
Adrenergic Symptoms
Adrenergic symptoms are the body’s initial response to low blood glucose and result from the release of adrenaline. These symptoms include:
- Tremors
- Palpitations
- Sweating
- Anxiety
- Hunger
Neuroglycopenic Symptoms
As blood glucose levels continue to drop, the brain’s glucose supply becomes insufficient, leading to neuroglycopenic symptoms. These symptoms can impair cognitive function and include:
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Headache
- Difficulty concentrating
- Slurred speech
- Blurred vision
- Seizures
- Loss of consciousness
Diagnosis of Hypoglycemia
The diagnosis of hypoglycemia involves confirming low blood glucose levels in the presence of symptoms and evaluating the underlying cause.
Whipple’s Triad
Whipple’s triad is a set of criteria used to diagnose hypoglycemia. It includes:
- Symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia.
- A low plasma glucose concentration measured at the time of the symptoms.
- Relief of symptoms after the plasma glucose level is raised.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are crucial for confirming hypoglycemia and identifying potential underlying causes. These tests include:
- Blood Glucose Measurement: To confirm low blood glucose levels.
- Insulin Levels: To evaluate insulin production and rule out insulinoma.
- C-peptide Levels: To distinguish between endogenous and exogenous insulin sources.
- Hormone Levels: To check for deficiencies in cortisol, growth hormone, and other hormones.
Imaging Studies
In cases where an insulinoma or other pancreatic pathology is suspected, imaging studies such as an MRI, CT scan, or endoscopic ultrasound may be necessary to identify the lesion.
Prevention and Management of Hypoglycemia
Preventing and managing hypoglycemia involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication adjustments, and education. Here are some strategies to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia:
Lifestyle Modifications
Regular Meals and Snacks
Eating regular meals and snacks that include carbohydrates can help maintain stable blood glucose levels. For individuals with diabetes, it is essential to match carbohydrate intake with insulin or medication doses.
Monitoring Blood Glucose Levels
Frequent blood glucose monitoring allows individuals to detect and address low blood sugar levels promptly. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) can provide real-time glucose readings and trends, aiding in better glucose management.
Balanced Physical Activity
Balancing physical activity with food intake and medication is crucial. Individuals engaging in strenuous exercise should consume additional carbohydrates and adjust their insulin doses as needed to prevent hypoglycemia.
Medication Adjustments
Insulin Therapy
For individuals on insulin therapy, precise titration and timing of insulin doses are critical. It is important to adjust insulin doses based on blood glucose readings, carbohydrate intake, and physical activity levels. Educating patients on how to make these adjustments can help prevent hypoglycemia.
Oral Hypoglycemic Agents
For those taking oral hypoglycemic agents, particularly sulfonylureas and meglitinides, dose adjustments may be necessary to avoid hypoglycemia. Switching to medications with a lower risk of hypoglycemia, such as DPP-4 inhibitors or SGLT2 inhibitors, may also be considered.
Education and Support
Patient Education
Educating patients about the symptoms, causes, and management of hypoglycemia is essential. Patients should be aware of the importance of regular meals, blood glucose monitoring, and recognizing early signs of hypoglycemia.
Support Systems
Having a support system in place, including family members, friends, and healthcare providers, can help individuals manage their condition more effectively. Support systems can provide assistance during hypoglycemic episodes and help with adherence to management plans.
Emergency Management of Severe Hypoglycemia
Severe hypoglycemia, characterized by confusion, unconsciousness, or seizures, requires immediate intervention. Here are the steps for emergency management:
Administering Glucose
For conscious individuals, consuming 15-20 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets, fruit juice, or regular soda, can quickly raise blood glucose levels. Blood glucose should be rechecked after 15 minutes, and the process repeated if necessary.
Glucagon Injection
For individuals who are unconscious or unable to consume carbohydrates, a glucagon injection can be administered. Glucagon is a hormone that raises blood glucose levels by stimulating the release of glucose from the liver. Training family members and caregivers on how to administer glucagon can be life-saving.
Emergency Medical Assistance
In cases where glucagon is not available or the individual does not respond to treatment, emergency medical assistance should be sought immediately. Paramedics can administer intravenous glucose to rapidly correct severe hypoglycemia.
See also: What’s the Relationship Between Stress and Hypoglycemia
Conclusion
Hypoglycemia is a condition that can affect both individuals with and without diabetes. Understanding the causes, risk factors, and preventive measures is essential for effective management. By maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and appropriate medication adjustments, individuals can reduce their risk of hypoglycemia. Education and support systems play a crucial role in helping individuals recognize and respond to hypoglycemic episodes. For those with diabetes, close monitoring of blood glucose levels and proactive management strategies are key to preventing and managing hypoglycemia.
Related topics:
Does Too Much Insulin Cause Hypoglycemia?