Blood glucose monitoring is a cornerstone in the management of diabetes, enabling individuals to maintain optimal blood glucose levels and prevent both short-term complications and long-term damage associated with the disease. The development of glucose monitors, particularly continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), has revolutionized diabetes care. This article delves into the mechanisms, technology, and advancements of glucose monitors, offering a comprehensive understanding of how they function.
The Basics of Blood Glucose Monitoring
The Importance of Blood Glucose Monitoring
Blood glucose monitoring is essential for people with diabetes to manage their condition effectively. It helps in:
Glycemic Control: Keeping blood sugar levels within a target range reduces the risk of complications.
Therapeutic Adjustments: Informing adjustments in diet, physical activity, and medication.
Preventing Hypoglycemia and Hyperglycemia: Immediate detection and correction of abnormal blood glucose levels.
Long-term Health: Reducing the risk of complications such as cardiovascular disease, neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy.
Types of Glucose Monitors
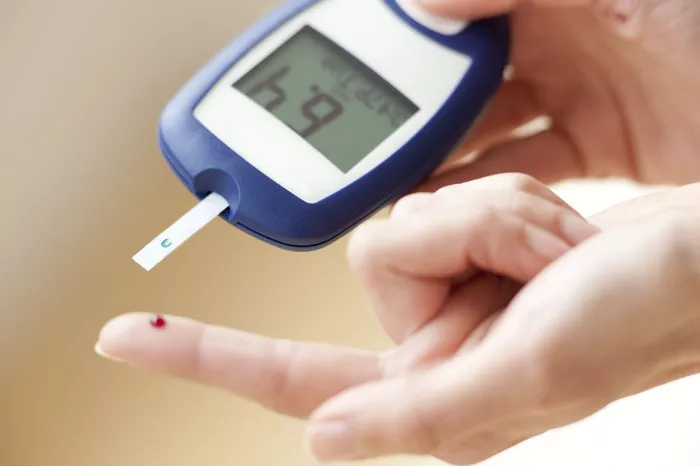
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG): Typically involves finger-prick tests to measure glucose levels using a portable glucometer.
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM): Uses a sensor inserted under the skin to provide real-time glucose readings.
How Glucometers Work
Components of a Glucometer
Test Strips: Contain chemicals that react with glucose in the blood.
Lancet: Used to prick the skin and obtain a blood sample.
Meter: Analyzes the blood sample and displays the glucose concentration.
The Chemistry of Blood Glucose Measurement
Enzymatic Reaction: Test strips typically use enzymes such as glucose oxidase or glucose dehydrogenase. When blood is applied to the strip, the enzyme reacts with glucose to produce gluconic acid.
Electrochemical Detection: The chemical reaction generates an electric current proportional to the glucose concentration. The meter measures this current and converts it into a digital readout.
The Process Step-by-Step
Pricking the Finger: A lancet device is used to obtain a small drop of blood.
Applying Blood to the Test Strip: The blood drop is placed on the test strip, initiating the enzymatic reaction.
Analyzing the Sample: The glucometer reads the electric signal produced by the reaction.
Displaying the Result: The glucose level is displayed on the meter’s screen within seconds.
Calibration and Accuracy
Coding and Calibration: Some glucometers require manual calibration or coding to match the test strips’ batch. Modern glucometers often come with pre-calibrated test strips.
Factors Affecting Accuracy: User technique, environmental conditions, and the hematocrit level (proportion of red blood cells) can affect accuracy.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
Components of a CGM System
Sensor: Inserted under the skin, it measures glucose levels in interstitial fluid.
Transmitter: Attached to the sensor, it sends data wirelessly to a receiver or smart device.
Receiver/Display Device: Displays real-time glucose readings and trends.
The Technology Behind CGMs
Interstitial Fluid Measurement: CGMs measure glucose in the interstitial fluid, which correlates closely with blood glucose but may lag by a few minutes.
Enzymatic Sensors: Like glucometers, CGM sensors use enzymes to react with glucose and produce an electrical signal.
Data Transmission and Display: The transmitter sends data to a receiver or smartphone app, providing continuous updates on glucose levels and trends.
Calibration and Accuracy of CGMs
Initial Calibration: Many CGMs require calibration with finger-prick blood glucose readings to ensure accuracy.
Improving Accuracy: Advances in sensor technology and algorithms have improved CGM accuracy, reducing the need for frequent calibrations.
Factors Influencing Accuracy: Sensor placement, skin temperature, and hydration can impact readings.
Advances in Glucose Monitoring Technology
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring
Optical Methods: Techniques such as near-infrared spectroscopy and Raman spectroscopy are being explored for non-invasive glucose monitoring.
Transdermal Systems: Using patches or devices that extract interstitial fluid non-invasively to measure glucose.
Integration with Insulin Delivery Systems
Closed-Loop Systems: Also known as artificial pancreas systems, these integrate CGMs with insulin pumps to automate insulin delivery based on real-time glucose readings.
Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems: These systems require user input for meal boluses but adjust basal insulin delivery automatically.
Improved Sensor Technology
Longer Wear Time: Newer sensors are designed to last longer, reducing the frequency of replacements.
Enhanced Biocompatibility: Advances in materials science have improved sensor biocompatibility, reducing irritation and increasing user comfort.
Reduced Calibration Needs: Enhanced algorithms and sensor technology have minimized the need for frequent calibrations, simplifying the user experience.
Future Directions in Glucose Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Predictive Analytics: AI algorithms can predict glucose trends and provide proactive alerts to prevent hypo- or hyperglycemia.
Personalized Insights: Machine learning can analyze individual glucose patterns and offer personalized recommendations for diet, exercise, and medication adjustments.
Wearable Technology
Smartwatches and Fitness Trackers: Integration of glucose monitoring with wearable devices for seamless health tracking.
Implantable Sensors: Long-term implantable sensors that provide continuous glucose monitoring without the need for frequent sensor changes.
Advances in Non-Invasive Monitoring
Improved Accuracy: Refinement of non-invasive technologies to achieve accuracy comparable to invasive methods.
User Convenience: Development of easy-to-use, pain-free devices to enhance user compliance and quality of life.
Challenges and Considerations in Glucose Monitoring
Ensuring Accuracy and Reliability
Quality Control: Regular testing and calibration to ensure devices remain accurate and reliable.
User Training: Educating users on proper device usage and maintenance to ensure accurate readings.
Addressing Accessibility and Affordability
Cost Considerations: Making glucose monitoring devices affordable and accessible to a broader population.
Insurance Coverage: Ensuring that insurance plans cover the costs of modern glucose monitoring technologies.
Overcoming Technical Challenges
Sensor Durability: Enhancing sensor durability to withstand wear and environmental factors.
Data Security: Ensuring the privacy and security of health data transmitted by CGMs and associated devices.
Conclusion
The evolution of glucose monitoring technologies has significantly improved the management of diabetes, providing individuals with the tools needed to maintain optimal blood glucose levels and enhance their quality of life. From the basic finger-prick glucometers to advanced continuous glucose monitoring systems and the promising future of non-invasive devices, the field continues to advance rapidly. As technology evolves, the focus remains on improving accuracy, convenience, and affordability to ensure that everyone with diabetes can benefit from these life-changing tools.
Related topics:
What Is A Normal Blood Sugar Level Before Breakfast