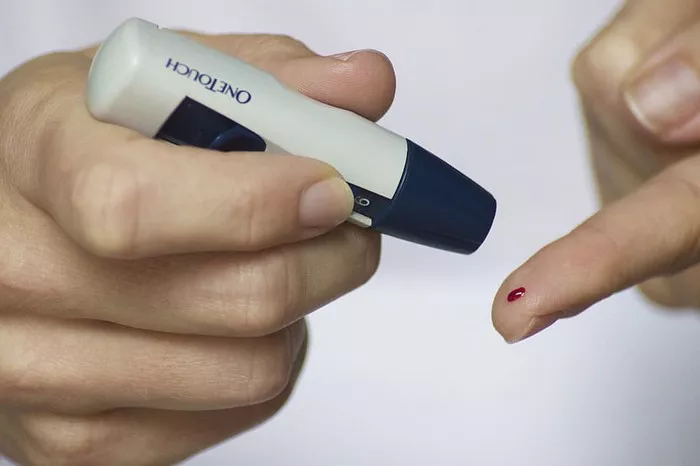
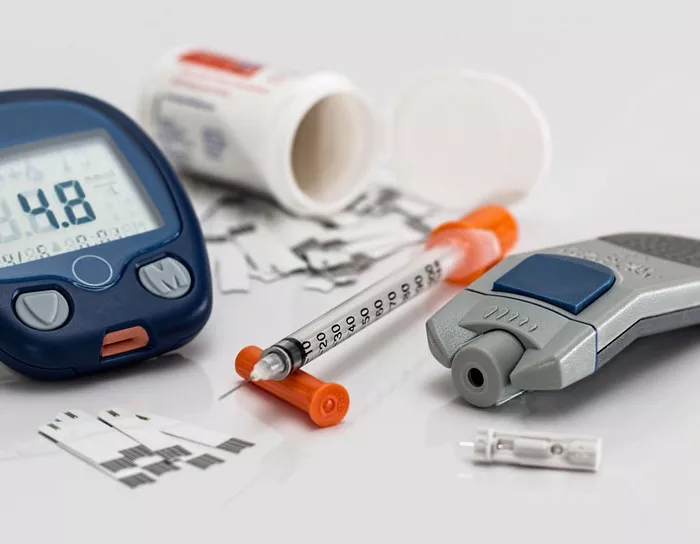
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. This condition results in elevated blood sugar levels, which can lead to a variety of complications if left untreated. Risk factors for type 2 diabetes include obesity, sedentary lifestyle, genetic predisposition, and certain medical conditions. Managing type 2 diabetes involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring to control blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Treatment Goals
The primary goals of type 2 diabetes treatment are to:
Maintain target blood sugar levels within a healthy range to prevent hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
Prevent or delay the onset of diabetes-related complications such as cardiovascular disease, kidney failure, neuropathy, and retinopathy.
Improve quality of life by reducing symptoms associated with diabetes and promoting overall health and well-being.
First-Line Medication: Metformin
Metformin is considered the first-line medication for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It belongs to a class of drugs called biguanides and works by reducing glucose production in the liver and increasing insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues. Benefits of metformin include:
Lowering blood sugar levels without causing excessive insulin secretion
Helping to prevent weight gain or promoting modest weight loss
Improving lipid profiles by lowering LDL cholesterol and triglycerides
Common side effects of metformin may include gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal discomfort. These side effects are usually mild and can often be managed by taking the medication with food or adjusting the dosage. In rare cases, metformin may cause lactic acidosis, a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
Additional Medications
When metformin alone is not sufficient to control blood sugar levels, healthcare providers may prescribe additional medications to complement treatment. These may include:
Sulfonylureas: Glipizide, glimepiride, and glyburide stimulate insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells, helping to lower blood sugar levels.
Meglitinides: Repaglinide and nateglinide work similarly to sulfonylureas by stimulating insulin secretion, but they have a shorter duration of action and may be taken with meals.
DPP-4 inhibitors: Saxagliptin, sitagliptin, linagliptin, and alogliptin increase insulin secretion and decrease glucagon production, resulting in lower blood sugar levels.
GLP-1 receptor agonists: Liraglutide and other GLP-1 agonists stimulate insulin secretion, inhibit glucagon production, slow gastric emptying, and promote weight loss.
SGLT2 inhibitors: Medications such as empagliflozin and canagliflozin block glucose reabsorption in the kidneys, causing excess glucose to be excreted in the urine.
In some cases, insulin therapy may be necessary to achieve target blood sugar levels. Insulin is typically reserved for individuals who have significant insulin resistance or progressive beta-cell failure despite oral medications.
Comparative Effectiveness
Clinical trials have compared the effectiveness of different medications for treating type 2 diabetes. For example, the Researching Cardiovascular Events with a Weekly Incretin in Diabetes (REWIND) trial compared the cardiovascular outcomes of dulaglutide (a GLP-1 receptor agonist) with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes. The study found that dulaglutide significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular events compared to placebo, highlighting the cardiovascular benefits of this medication class.
Another study, the Liraglutide Effect and Action in Diabetes: Evaluation of Cardiovascular Outcome Results (LEADER) trial, compared the cardiovascular outcomes of liraglutide (another GLP-1 receptor agonist) with placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk. The study found that liraglutide reduced the risk of cardiovascular events, cardiovascular death, and all-cause mortality compared to placebo, demonstrating the cardiovascular benefits of this medication.
Lifestyle Modifications
In addition to medication, lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing type 2 diabetes. These may include:
Following a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats
Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, swimming, or strength training
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly and adjusting diet, exercise, and medication as needed
Avoiding tobacco use and limiting alcohol consumption
Managing stress through relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or counseling
Monitoring and Adjustment
Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels is essential for assessing treatment effectiveness and making adjustments as needed. Healthcare providers may recommend self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) for more comprehensive data. Based on blood sugar readings and other clinical parameters, healthcare providers can make informed decisions about medication adjustments, lifestyle modifications, and additional interventions to optimize diabetes management.
Potential Side Effects
While medications for type 2 diabetes are generally well-tolerated, they may cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects may include:
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar)
Gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, diarrhea, or constipation
Weight gain or loss
Hypersensitivity reactions such as rash or itching
It is essential to discuss any concerns or side effects with a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.
Consultation with Healthcare Providers
Individuals with type 2 diabetes should consult with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan based on their specific needs and goals. Healthcare providers can offer guidance, support, and monitoring to ensure optimal diabetes management and reduce the risk of complications. Open communication and collaboration between patients and healthcare providers are essential for achieving treatment goals and maintaining overall health and well-being.
Resources and References
For further reading and research on type 2 diabetes treatment, consider exploring reputable sources such as:
American Diabetes Association (ADA)
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
ClinicalTrials.gov for information on ongoing clinical trials
Peer-reviewed journals such as Diabetes Care, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, and JAMA
Conclusion
Managing type 2 diabetes involves a multifaceted approach that includes medication, lifestyle modifications, regular monitoring, and consultation with healthcare providers. Metformin is typically recommended as the first-line medication for type 2 diabetes, with additional medications prescribed as needed to achieve target blood sugar levels and prevent complications. Personalized treatment plans, based on individual health profiles and preferences, are essential for optimizing diabetes management and improving quality of life. By working closely with healthcare providers, individuals with type 2 diabetes can develop effective strategies for managing their condition and achieving better health outcomes.
Related Topics:
What Fruit Can I Eat With Diabetes Type 2?