In discussions surrounding metabolic health and diabetes management, terms like “blood sugar” and “glucose” are often used interchangeably, yet they represent distinct concepts with unique implications for health and well-being. While both are closely related to glucose metabolism, understanding the differences between blood sugar and glucose is essential for accurate communication, diagnosis, and management of metabolic conditions. In this comprehensive article, we delve into the fundamental distinctions between blood sugar and glucose, their physiological underpinnings, measurement methods, and clinical significance.
1. Glucose:
Glucose is a simple sugar and the primary source of energy for cells throughout the body. It is a carbohydrate molecule that is essential for various physiological processes, including cellular respiration, ATP production, and metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is derived from the digestion and breakdown of dietary carbohydrates, including sugars, starches, and fiber, and is absorbed into the bloodstream through the gastrointestinal tract.
Key Aspects of Glucose:
- Physiological Role: Glucose serves as the primary fuel source for cellular metabolism, providing energy for essential processes such as brain function, muscle contraction, and organ function.
- Metabolism: Glucose metabolism involves the breakdown of glucose molecules through glycolysis, citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle), and oxidative phosphorylation to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the body’s primary energy currency.
- Regulation: Glucose levels are tightly regulated by various hormones, including insulin, glucagon, cortisol, and epinephrine, to maintain optimal blood glucose concentrations and prevent hypo- or hyperglycemia.
2. Blood Sugar:
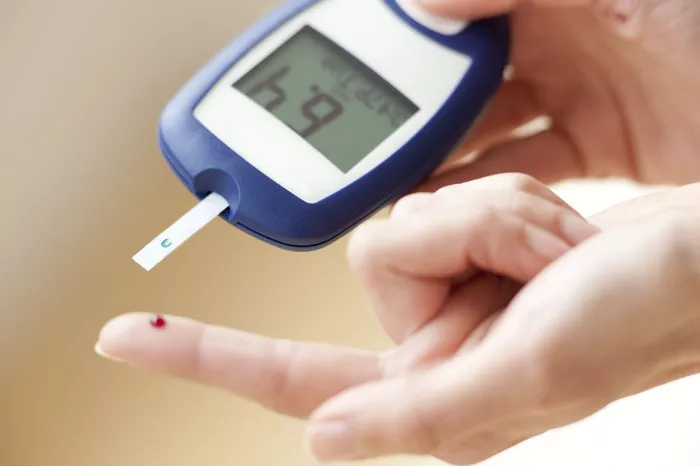
Blood sugar refers to the concentration of glucose molecules present in the bloodstream at a given time. It encompasses various forms of sugars circulating in the blood, including glucose, fructose, and galactose, although glucose is the most abundant and readily measurable sugar. Blood sugar levels fluctuate in response to dietary intake, hormonal fluctuations, physical activity, stress, and metabolic processes.
Key Aspects of Blood Sugar:
- Composition: Blood sugar consists of glucose and other sugars present in the bloodstream, reflecting the overall carbohydrate metabolism and homeostasis in the body.
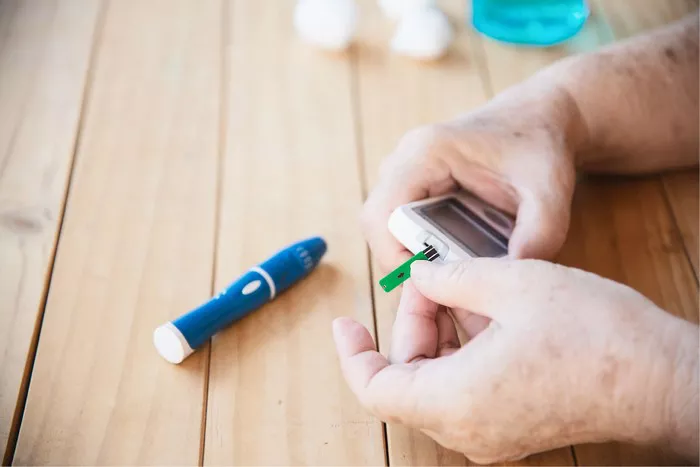
- Measurement: Blood sugar levels are typically measured using a glucose meter and fingerstick blood samples obtained from capillary blood. The glucose meter quantifies the amount of glucose present in the blood sample, providing a numerical value in units of milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
- Clinical Significance: Monitoring blood sugar levels is essential for individuals with diabetes to evaluate their glycemic control, identify patterns and trends, and adjust treatment regimens accordingly. Target blood sugar ranges may vary based on individual factors such as age, comorbidities, treatment goals, and lifestyle factors.
3. Key Differences Between Glucose and Blood Sugar:
While glucose and blood sugar are related concepts, they represent different aspects of carbohydrate metabolism and have distinct implications for health and disease:
- Physiological Concept: Glucose specifically refers to the molecular form of sugar utilized for cellular metabolism, whereas blood sugar encompasses various sugars present in the bloodstream, including glucose, fructose, and galactose.
- Measurement Method: Glucose levels are measured directly using enzymatic assays or spectrophotometry, whereas blood sugar levels are measured indirectly using glucose meters that quantify glucose concentrations in blood samples.
- Clinical Application: Glucose testing provides real-time information about blood glucose levels at a specific point in time and is used for day-to-day management of diabetes. Blood sugar monitoring offers insights into overall carbohydrate metabolism and glycemic control and is used to assess long-term trends and treatment adherence.
4. Clinical Utility and Implications:
Both glucose and blood sugar monitoring are essential components of diabetes management and play crucial roles in optimizing glycemic control and preventing complications associated with dysglycemia:
- Glucose Monitoring: Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels helps individuals with diabetes track their glycemic control, identify patterns, and make informed decisions about treatment adjustments, dietary choices, and physical activity.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Blood sugar monitoring provides insights into overall carbohydrate metabolism and glycemic control over time and guides treatment goals, risk stratification, and interventions to prevent long-term complications associated with diabetes.
5. Conclusion:
In conclusion, while glucose and blood sugar are related concepts, they represent different aspects of carbohydrate metabolism and provide distinct information about glycemic control and health status. Glucose refers specifically to the molecular form of sugar utilized for cellular metabolism, whereas blood sugar encompasses various sugars present in the bloodstream, reflecting overall carbohydrate metabolism and homeostasis. By understanding the differences between glucose and blood sugar, healthcare providers and individuals with diabetes can effectively monitor glycemic control, optimize treatment regimens, and improve long-term health outcomes.