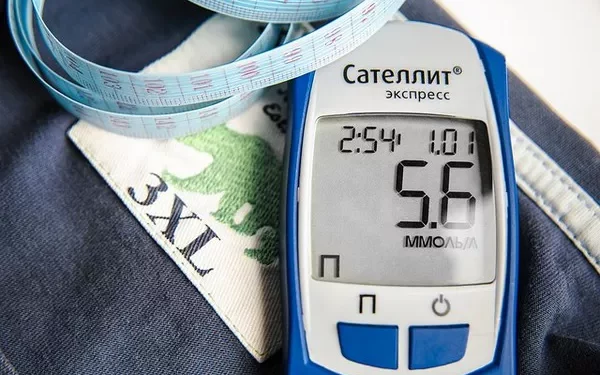
Monitoring ketone levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes, especially to prevent diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). While glucose meters are commonly used to measure blood sugar, certain models also allow for ketone testing. This article provides a detailed guide on how to check ketone levels using a glucose meter, ensuring accurate readings and effective diabetes management.
Understanding Ketones and Their Importance
Ketones are chemicals produced when the body breaks down fat for energy. In people with diabetes, high ketone levels can indicate insufficient insulin, leading to DKA—a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention. Regular monitoring helps in early detection and prevention.
Choosing the Right Glucose Meter
Not all glucose meters can test for ketones. It’s essential to select a meter designed for both glucose and ketone measurements. Some reliable options include:
Abbott Precision Xtra: Measures β-hydroxybutyrate, the primary ketone body in the blood. Requires specific ketone test strips for accurate results.
FreeStyle Optium Neo: Offers dual testing for glucose and ketones, providing quick and precise readings.
Keto-Mojo GK+: Designed for ketogenic diet monitoring, it accurately measures both glucose and ketone levels.
Ensure you use the correct test strips compatible with your chosen meter to avoid inaccurate readings.
Preparing for the Test
Before testing, gather the necessary supplies:
- Glucose meter capable of ketone testing
- Ketone test strips specific to your meter
- Lancing device and sterile lancets
- Alcohol swabs
- Clean tissue or cotton ball
Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and warm water. Dry them completely to prevent dilution of the blood sample.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Ketone Levels
Insert the Ketone Test Strip: Place the ketone-specific test strip into the meter. The device should recognize the strip and prepare for testing.
Prepare the Lancing Device: Load a sterile lancet into the lancing device. Adjust the depth setting if necessary.
Clean the Puncture Site: Use an alcohol swab to clean the side of your fingertip. Allow it to air dry completely.
Obtain a Blood Sample: Press the lancing device against the side of your fingertip and activate it to obtain a drop of blood.
Apply Blood to the Test Strip: Touch the edge of the test strip to the blood drop. The strip will draw in the blood via capillary action.
Wait for the Result: The meter will analyze the sample and display your ketone level, usually within 10 seconds.
Interpreting Ketone Levels
Understanding your ketone readings is vital:
Below 0.6 mmol/L: Normal range. No action needed.
0.6 to 1.5 mmol/L: Slightly elevated. Monitor closely and consider adjusting your insulin or diet.
1.6 to 3.0 mmol/L: High. Contact your healthcare provider for guidance.
Above 3.0 mmol/L: Very high. Seek immediate medical attention as this may indicate DKA.
When to Test Ketone Levels
Regular testing helps in early detection of potential issues. Consider testing when:
- Your blood sugar is consistently above 13.9 mmol/L (250 mg/dL).
- You experience symptoms like nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or rapid breathing.
- You are ill, stressed, or have an infection.
- You are on a ketogenic diet and want to monitor your state of ketosis.
Tips for Accurate Testing
- Always use fresh, unexpired test strips.
- Store test strips in a cool, dry place.
- Ensure your meter is calibrated correctly.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for your specific meter model.
- Keep a log of your readings to track patterns and share with your healthcare provider.
Integrating Ketone Testing into Diabetes Management
Regular ketone testing complements blood sugar monitoring and helps in making informed decisions about insulin dosage, diet, and exercise. It is an essential component of a comprehensive diabetic diet plan, ensuring overall health and well-being.
Conclusion
Monitoring ketone levels using a compatible glucose meter is a straightforward process that plays a critical role in diabetes management. By understanding how to test accurately and interpret the results, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent complications like DKA. Always consult with your healthcare provider to tailor testing routines to your specific needs.
Related topics:
How to Find Blood Sugar Level in a Blood Test