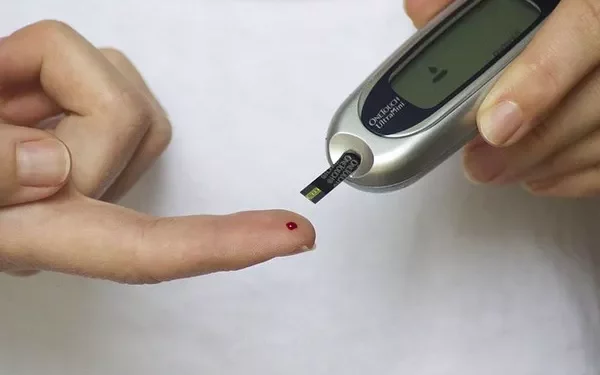
Glucometers are indispensable tools for individuals managing diabetes. They allow users to monitor their blood glucose levels conveniently and accurately, enabling effective diabetes management. This article delves into the science and technology behind glucometers, explaining how they measure glucose and the various factors influencing their accuracy. Understanding these mechanisms can help users make the most of their glucometers and better manage their condition.
Introduction to Glucometers
A glucometer, also known as a blood glucose meter, is a portable device used to measure the concentration of glucose in the blood. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is crucial for individuals with diabetes to maintain their health and prevent complications. Glucometers provide real-time feedback on blood sugar levels, allowing for timely adjustments in diet, exercise, and medication.
The Science Behind Glucose Measurement
Glucometers operate based on various principles of chemistry and electronics. The primary goal is to detect and quantify the amount of glucose present in a blood sample. Here’s a detailed look at how glucometers measure glucose:
1. Blood Sample Collection
The process begins with the collection of a blood sample, which is typically obtained by pricking the fingertip with a lancet. This method is commonly referred to as capillary blood sampling. The blood sample is then applied to a test strip, which is inserted into the glucometer.
2. Test Strip Composition
Test strips are a critical component of glucometers. They are designed to interact with the blood sample and facilitate glucose measurement. The typical test strip consists of several layers:
Lancing Area: The area where the blood sample is deposited.
Reaction Zone: Contains chemicals that react with glucose in the blood.
Electrode: Measures the electrical signal generated by the chemical reaction.
3. Electrochemical Method
Most modern glucometers use an electrochemical method to measure glucose levels. Here’s how it works:
Glucose Reaction: When the blood sample interacts with the chemicals on the test strip, a reaction occurs that produces a measurable electrical current. The specific chemicals used are typically glucose oxidase or glucose dehydrogenase, which react with glucose to produce hydrogen peroxide or another byproduct.
Current Measurement: The reaction generates an electrical current that is proportional to the amount of glucose in the blood sample. The electrodes on the test strip measure this current.
Signal Conversion: The electrical current is converted into a glucose concentration reading by the glucometer’s internal electronics. This conversion is done through complex algorithms that factor in the specific characteristics of the test strip and the sample.
4. Optical Method
Some glucometers use optical methods for glucose measurement. These devices use light to analyze the blood sample. Here’s how optical glucometers work:
Light Transmission: The glucometer shines light through the blood sample on the test strip.
Absorption Analysis: Different wavelengths of light are absorbed by glucose in the blood differently. The glucometer measures the light absorption at specific wavelengths to determine the glucose concentration.
Data Interpretation: The glucometer’s electronics interpret the light absorption data and calculate the glucose level.
Factors Affecting Glucometer Accuracy
The accuracy of a glucometer can be influenced by various factors, including:
1. Test Strip Quality
Manufacturing Variations: Variations in test strip manufacturing can affect accuracy. It is essential to use test strips that are compatible with your glucometer and within their expiration date.
Storage Conditions: Test strips should be stored in a cool, dry place. Exposure to moisture, heat, or light can affect their performance.
2. Blood Sample Quality
Sample Size: Using the correct amount of blood is crucial for accurate results. Too little or too much blood can lead to erroneous readings.
Contamination: Any contaminants on the test strip or blood sample can affect the measurement. Ensure hands and equipment are clean before testing.
3. User Technique
Proper Technique: Following the manufacturer’s instructions for sample collection and handling is vital. Improper technique can lead to inaccurate results.
Calibration: Some glucometers require calibration with a control solution. Regular calibration ensures the device remains accurate over time.
4. Environmental Factors
Temperature: Extreme temperatures can affect the performance of test strips and glucometers. Always use the device within the recommended temperature range.
Altitude: High altitudes can influence the accuracy of glucose measurements. Adjustments may be necessary for accurate readings.
Advances in Glucometer Technology
Recent advancements in glucometer technology aim to improve accuracy, ease of use, and overall user experience. Some notable innovations include:
1. Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
Real-Time Monitoring: CGMs provide continuous monitoring of glucose levels throughout the day and night. They use a small sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in interstitial fluid.
Data Integration: CGMs transmit data to a receiver or smartphone app, offering real-time feedback and trends in glucose levels.
2. Non-Invasive Glucometers
Alternative Technologies: Researchers are exploring non-invasive methods for glucose monitoring, such as infrared spectroscopy and radiofrequency. These technologies aim to measure glucose levels without the need for blood samples.
Future Prospects: While non-invasive glucometers are still in development, they hold promise for more convenient and less invasive glucose monitoring in the future.
3. Smart Glucometers
Enhanced Features: Smart glucometers come with features like Bluetooth connectivity, data tracking, and integration with health apps. They provide users with detailed insights into their glucose levels and trends.
Data Management: These devices can store historical data and generate reports, helping users and healthcare providers make informed decisions.
Proper Use and Maintenance of Glucometers
To ensure accurate readings and prolong the lifespan of your glucometer, follow these guidelines:
1. Regular Calibration
Calibration with Control Solutions: Use control solutions as recommended by the manufacturer to check the accuracy of your glucometer. Regular calibration helps maintain reliable results.
Follow Manufacturer Instructions: Adhere to the calibration schedule and procedures specified in the user manual.
2. Proper Storage
Store Test Strips Correctly: Keep test strips in their original container and store them in a cool, dry place. Avoid exposure to extreme temperatures and humidity.
Clean the Device: Clean the glucometer as instructed to prevent contamination and ensure proper functioning.
3. Handling Blood Samples
Use Fresh Samples: Test blood samples promptly after collection. Delays can affect the accuracy of the results.
Follow Testing Instructions: Apply the blood sample to the test strip as directed by the manufacturer to avoid errors.
See also: What Is Glucose Level in Blood Work?
Conclusion
Glucometers are vital tools for managing diabetes, providing essential data on blood glucose levels. Understanding how glucometers measure glucose—through electrochemical or optical methods—helps users appreciate the technology behind these devices and their importance in diabetes management.
Factors such as test strip quality, blood sample handling, and user technique can influence the accuracy of glucose measurements. Advances in technology, including continuous glucose monitoring and smart glucometers, are enhancing the way individuals track and manage their blood sugar levels.
Proper use and maintenance of glucometers are crucial for accurate readings and effective diabetes management. By adhering to best practices, individuals with diabetes can make informed decisions about their health and improve their quality of life.
This comprehensive understanding of glucometer functionality and accuracy empowers users to make the most of their devices, ensuring effective diabetes management and better health outcomes.
Related topics:
What Glucose Number Indicates Diabetes?